Zinc is essential to life. It is a natural element found in all plants and animals and plays a crucial part in the health of our skin, teeth, bones, hair, nails, muscles, nerves and brain.
Prevalence of zinc deficiency
Worldwide zinc deficiency could rival the documented iron deficiency. Up to one-fifth of the worlds people may lack sufficient zinc in their diet, while an estimated one-third live in countries considered at high risk of Zinc deficiency.
| low birth weight | weight loss | penumonia |
| delayed sexual development | infections | stretch marks |
| loss of smell and tastesensation | small breast in females | poor immune function |
| diminished wound healing | growth retardation | reduced collagen |
| anorexia | dwarfism | macular degeneration |
| loss of appetite | delayed puberty in adolsescents | arthritic problems |
| depression | rough skin | cataracts |
| strong body odor | poor appetite | optic neuritis |
| benign prostatic hypertropy | mental lethargy | skin conditions such as acne and dermatitis |
| impotence | short stature | defective bone mineralization |
| some hair, nail and joint condition | diarrhea |
Zinc & Human health
- Skin & hair health
Approximately 9 % of the zinc content of the body is associated with the skin.
Zinc plays an important role in the three skin functions:
- Morphogenesis
- Repair and maintenance
- Protection and defense
Zinc is effective in controlling the formation of:
- Acne lesions
- Rosacea
- Eczemas
- Ulcers
- Alopecia
- Erosive Pustular Dermatosis of Scalp.
- The formation of a pro-tumorigenic inflammatory microenvironment and impaired host defences against skin carcinogenesis that facilitate carcinoma development.
Improve fertility in men

Infertility affects 15% of couples globally, amounting to 48.5 million couples annually.
Males solely account for 20-30% of infertility cases and are responsible for 50% of all infertile cases.
Approximately 25% of infertile men present elevated levels of ROS in the semen and often lower antioxidant capacity of semen.
Zinc is necessary to:
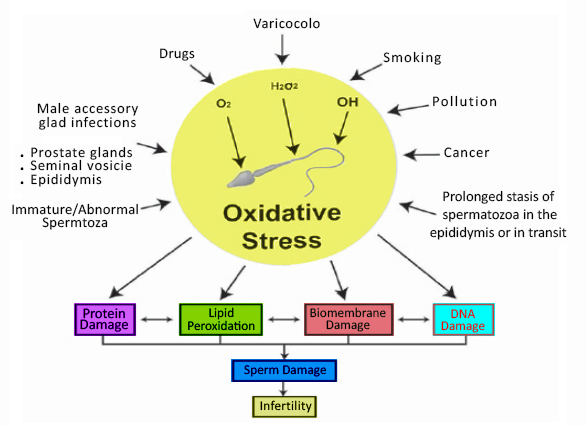
- Maintain normal serum testosterone.
- Inhibit the aromatase enzyme that converts testosterone into excess estrogen.
- Increase sperm count and motility
- As an antioxidant, play a role in maintaining the functional life span of ejaculated sperm and improve fertility
Immune system booster
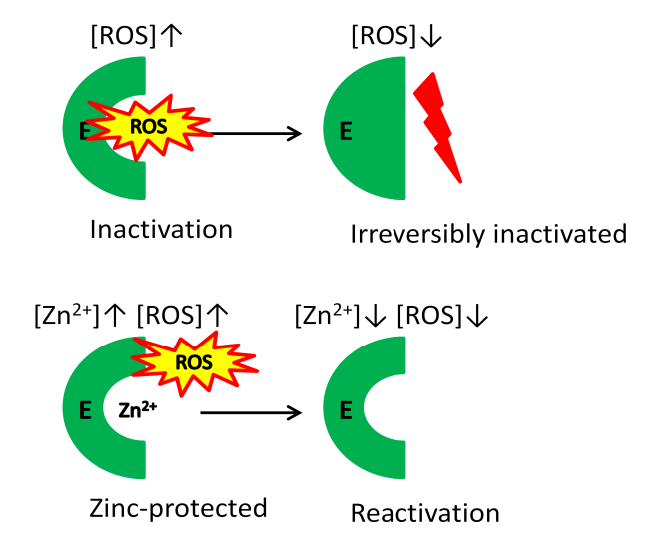
Zinc plays an important role in:
Regulating the production of cells in the body's immune system, which protects against infection and disease.
Improve brain and mental function
Zinc deprivation influences brain zinc homeostasis and leads to:
- Enhance memory, thinking skills and learning
- Improve function of the nervous system and behavior (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, bipolar disorder, depression, schizophrenia)
Bone Health
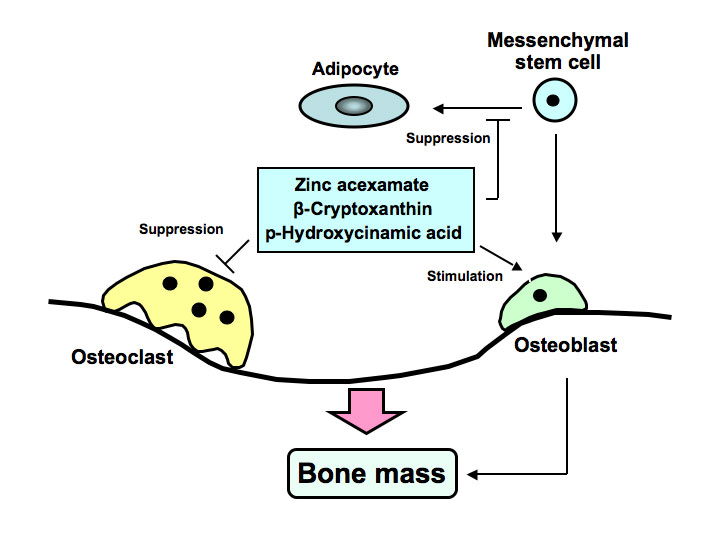
A significant positive correlation between bone zinc content and bone strength suggests that zinc may play an important role in bone health.
Zinc is needed for:
- Osteoblastic activity
- Collagen synthesis
Improve the symptoms of aging:
The supply of zinc is considered necessary in aging:
- Improvement of immune functions
- Prevention age-related degenerative diseases
- Improvement stress response systems
Cardiovascular system health:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide.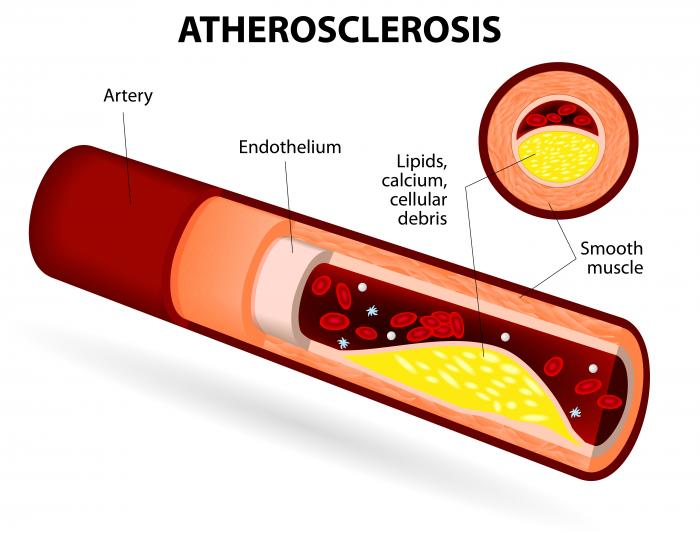
Zinc is critical in:
- Blood clotting
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as: arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, congestive heart failure , coronary heart disease and anemia
Diabetes control
There appears to be a complex interrelationship between Zinc and both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Zinc is very important in:
- The synthesis, storage, and secretion of insulin
- Maintaining conformational integrity of insulin in the hexametric form.
Cancer prevention
Zinc as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent plays a pivotal role in host defense against the initiation and promotion of several malignancies.
Vitamin C

Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a water-soluble vitamin that is necessary for normal growth and development.
It is an antioxidant that helps maintain the connective tissue protein collagen in bones, cartilage, muscle, and blood vessels, protects against infection, and helps iron absorption.
Clinical trials of vitamin C supplementation have demonstrated a protective effect of vitamin C in health and disease, such as:
- Bone Healing
- Cancer prevention
- Age-Related Eye Diseases prevention
- Alzheimer’s disease control
- Skin health & Collagen production
- Diabetes control
- Anemia prevention
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Immune system booster
- Gallbladder disease prevention.
Recommendations
The best way to get the daily requirement of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C and zinc, is to eat Vivatune zinc plus C pellet.
Viva Tune® zinc plus Time Released is a unique formula that provides controlled release of zinc and Vitamin C over a prolonged period of time to keep this water-soluble vitamin more available for your body cells and reduces dosing frequency.
Viva Tune® zinc plus has Double antioxidant function in a capsule and support energy production, immune system booster, bone health, improve fertility in men and skin & hair health.
Packaging:
60 Capsules, 300 mg Vitamin C + 5 mg Zinc, Delayed release pellets
Directions:
Take one capsule daily with a glass of water or as recommended by a health-care practitioner.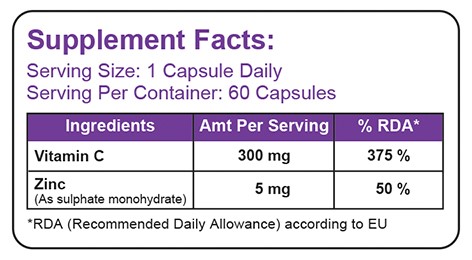
References:
- Bhowmik D, et al. A potential medicinal importance of zinc in human health and chronic disease. Int J Pharm Biomed Sci. 2010; 1(1):05-11
- Houshiar-rad N, et al. Zinc intake pattern in Iranian households and risk of zinc deficiency at national level. Iranian Journal of Nutrition Sciences & Food Technology. 2013;7(7):409-420.
- Emri G, et al. Skin carcinogenesis: the pathogenetic and therapeutic role of zinc. Journal of Metallomics and Nanotechnologies. 2015; 2: 19-26.
- Richelle M, et al. Skin bioavailability of dietary vitamin E, carotenoids, polyphenols, vitamin C, zinc and selenium. British Journal of Nutrition. 2006; 96: 227–238.
- Gupta M, et al. Zinc Therapy in Dermatology: A Review. Dermatology Research and Practice · 2014; 1-11.
- Kumar N, et al. Role of Zinc in Male Infertility: Review of Literature. Indian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology Research .2016; 3(2):167-171.
- Ghareeb D, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Male Fertility and Idiopathic Infertility: Causes and Treatment. Journal of Diagnostic Techniques & Biomedical Analysis.2014; 3(1):1-12.
- Kumar V,et al. Zinc Deficiency and Its Effect on the Brain: An Update. International Journal of Molecular Genetics and Gene Therapy.2016;1(1):1-7.
- Mahdaviroshan M, et al. Effect of zinc supplementation on serum zinc and calcium levels in postmenopausal osteoporotic women in Tabriz, Islamic Republic of Iran. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2013; 19(3):271-275.
- Masayoshi Yamaguchi. Nutritional zinc plays a pivotal role in bone health and osteoporosis prevention. Edorium J Nutr Diet. 2015;1:1–8.
- Chasapis Ch, et al. Zinc and human health: an update. Arch Toxicol .2012; 86:521–534.
- Prasad A. Zinc: role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care .2009; 12: 646–652.
- Kaur K, et al. Zinc: The Metal of Life. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety.2014;13: 358-376.
- Angel Merlos Rodrigo M, et al. Zinc and metallothionen in prostate cancer: A review. Journal of Metallomics and Nanotechnologies .2015; 2: 58—63.
- Samer A,et al. Vitamin C in Health and Disease. The journal of contemporary dental practice. 2004; 2(5): 001-013.